The proportional term produces an output value that is proportional
to the current error value. The proportional response can be adjusted by
multiplying the error by a constant Kp, called the proportional gain constant.
The proportional term is given by:
A high proportional gain results in a large change in the output for a
given change in the error. If the proportional gain is too high, the
system can become unstable (see the section on loop tuning).
In contrast, a small gain results in a small output response to a large
input error, and a less responsive or less sensitive controller. If the
proportional gain is too low, the control action may be too small when
responding to system disturbances. Tuning theory and industrial practice
indicate that the proportional term should contribute the bulk of the
output change.

 06.32
06.32
 Unknown
Unknown
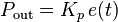
 Posted in
Posted in

